Introduction
Lightroom App Latest Version Apk In the contemporary digital age, photography has evolved far beyond the limitations of film, darkrooms, and chemical processes. The democratization of visual creation, facilitated by smartphones, affordable cameras, and accessible editing tools, has reshaped how individuals capture, refine, and share images. Among the numerous software solutions available, Adobe Lightroom stands as one of the most influential and widely used applications for photographers, designers, social media creators, and visual storytellers. As part of Adobe’s Creative Cloud ecosystem, Lightroom distinguishes itself through its powerful combination of non-destructive editing, organizational efficiency, and user-friendly interface. The application’s availability across multiple devices—desktop, mobile, and web—cements its importance as a tool that meets both professional demands and casual creative exploration.
This essay explores the Lightroom app in depth, tracing its origins, technical capabilities, interface, creative potential, workflow optimization strategies, integration with modern technology, and its broader cultural and professional impact on photography. As digital imagery continues its rapid evolution, Lightroom remains one of the most adaptive and vital pillars supporting the global photography community.
Chapter 1: The Evolution of Adobe Lightroom
1.1 Origins and Early Development
Adobe Lightroom originated from the need to organize and process the enormous influx of digital images produced by photographers in the early 2000s. Traditional editing tools—most notably Adobe Photoshop—provided unparalleled power but lacked efficient photo cataloging features. Professional photographers needed a dedicated solution to import, sort, categorize, and edit hundreds or thousands of images in a streamlined manner.
Adobe began developing Lightroom under the codename “Shadowland”, with the goal of integrating powerful photo editing tools into a workflow-centered environment. The first public beta was released in January 2006, marking a new chapter in digital image management. Lightroom quickly distinguished itself by offering:
- Non-destructive editing
- An intuitive user interface
- Effective image cataloging and keyword tagging
- Simplified batch editing
- A modular workspace
These innovations allowed photographers to accelerate their workflows while maintaining full image quality and control.
1.2 From Desktop to Mobile
In 2014, Adobe released Lightroom Mobile, transforming mobile devices into fully capable editing stations. While smartphones had already become major tools for capturing images, they lacked professional-grade editing capabilities. Lightroom Mobile introduced:
- Sync across devices via Creative Cloud
- Presets that could be shared between desktop and mobile
- RAW editing on mobile devices
- Advanced local adjustments
The mobile app redefined the relationship between photography and mobility, giving users the ability to shoot, edit, and publish from anywhere.
1.3 Cloud-Based Ecosystem
Lightroom Classic and the newer cloud-based Lightroom were eventually separated into two distinct products:
- Lightroom Classic retained the library-based system favored by professional desktop users.
- Lightroom (cloud-based) embraced automatic syncing, mobile-first workflows, and device flexibility.
This split allowed Adobe to satisfy two audiences simultaneously: traditional photographers and modern creators who prefer cloud integration and mobile editing.
Chapter 2: Core Features and Functional Capabilities
2.1 Non-Destructive Editing
One of Lightroom’s most celebrated features is its non-destructive editing, which preserves the original image file while applying changes through metadata instructions. This method:
- Protects the integrity of the original photograph
- Enables unlimited experimentation
- Allows users to revert or selectively undo any adjustment
Non-destructive editing fundamentally changes how users approach creativity by reducing risk and encouraging exploratory workflows.
2.2 Importing, Cataloging, and Organizing
The organizational capabilities of Lightroom are central to its appeal. Users can:
- Import images directly from cameras, memory cards, or mobile devices
- Add metadata such as keywords, titles, and copyright information
- Create collections and smart collections
- Use facial recognition to identify and group subjects
- Filter images by flags, stars, colors, dates, lenses, or camera settings
For professional photographers managing wedding archives or studio sessions, these tools are indispensable.
2.3 Global Adjustments
Lightroom’s global editing tools allow users to alter the overall appearance of an image, including:
- Exposure
- Contrast
- Highlights and shadows
- Whites and blacks
- Clarity and texture
- Vibrance and saturation
- Tone curves
- HSL (Hue, Saturation, Luminance)
These adjustments serve as the foundation of nearly every editing workflow.
2.4 Local Adjustments
More advanced users depend heavily on Lightroom’s local adjustment tools:
- Brush tool
- Graduated filter
- Radial filter
- Healing tool
- Range masks (color and luminance)
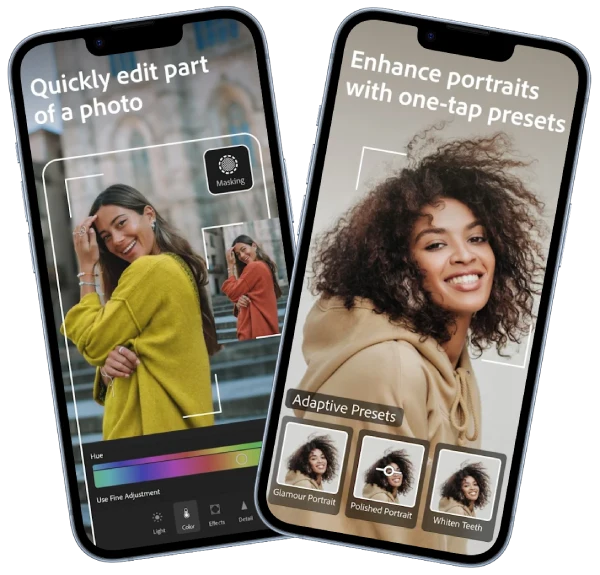
- AI-powered subject and sky selection
These tools offer control over specific parts of an image, enabling precision retouching, lighting adjustments, or creative effects.
2.5 Presets and Profiles
Presets allow users to apply predefined looks to images with a single click. Lightroom contains both Adobe-developed and user-created presets, offering styles such as:
- Film emulation
- High-contrast editorial
- Warm cinematic tones
- Black and white aesthetics
Presets have influenced social media culture significantly, creating recognizable editing trends across platforms like Instagram and TikTok.
2.6 RAW Editing on Mobile
The ability to edit RAW files on mobile devices once seemed unrealistic due to file size and processing demands. Lightroom Mobile changed this reality by enabling:
- Full RAW support
- Pro camera capture in RAW formats
- Device-level optimization
- Cloud syncing for large files
This feature democratized advanced mobile photography.
Chapter 3: Lightroom’s User Interface and Usability
3.1 Clean and Intuitive Design
Lightroom’s interface prioritizes clarity through:
- Minimalist layout
- Logical panel organization
- Seamless module transitions
- Dark mode environment conducive to image editing
This makes the app accessible even to beginners.
3.2 Mobile UI Experience
On mobile devices, Lightroom maintains ease of use by:
- Offering gesture-based adjustments
- Maintaining consistent iconography across platforms
- Providing tutorials, guided edits, and discoverable workflows
This ensures that users can navigate the app regardless of their experience level.
3.3 Usability for All Skill Levels
Lightroom offers value to a full spectrum of users:
- Beginners: One-click presets, auto adjustments, tutorials
- Intermediate users: Local adjustments, healing tools, color grading
- Professionals: Batch processing, lens corrections, RAW workflow, ICC profile management
Its scalability is one reason for widespread adoption.
Chapter 4: Creative Potential and Artistic Expression
4.1 Color Grading and Mood Creation
Color plays a major role in storytelling. Lightroom offers cinematic color grading through:
- Three-way color wheels
- Split toning
- HSL precision
- Custom profiles
Artists can create distinct moods, whether warm sunsets, moody shadows, or pastel-inspired aesthetics.
4.2 Black and White Photography
Lightroom App Latest Version Apk Lightroom excels in monochrome editing, offering precise control over luminance values across color channels. This results in black-and-white images with strong texture, depth, and emotional impact.
4.3 Skin Retouching and Portrait Editing
Lightroom’s portrait tools make professional retouching achievable without Photoshop. Tools like:
- Texture reduction
- Clarity control
- Healing brush
- AI masking for faces
allow for polished, natural-looking edits.
4.4 Landscape and Travel Photography
Landscape photographers benefit from Lightroom’s:
- Dehaze tool
- Sky enhancement
- Detail sharpening
- Lens corrections
These tools reveal depth, atmosphere, and vibrancy in scenic images.
4.5 Mobile Creativity
With Lightroom Mobile, creativity becomes spontaneous. Users can edit photos during travel, capture unique moments, and share in real-time without losing professional quality.
Chapter 5: Lightroom in Professional Workflow
5.1 Event Photography
Wedding and event photographers rely heavily on Lightroom because of:
- Fast batch processing
- Metadata templates
- Syncing adjustments across hundreds of images
- Efficient culling tools
This dramatically reduces turnaround times for clients.
5.2 Commercial and Studio Work
In commercial environments, Lightroom aids in:
- Tethered shooting
- Color consistency
- Catalog management
- Pre-client review processes
Its nondestructive pipeline is ideal for commercial revisions.
5.3 Social Media Content Creation
Influencers and content creators use Lightroom to develop consistent visual branding. Presets ensure cohesive aesthetics across a feed.

Chapter 6: Integration with Broader Technology and Ecosystems
6.1 Creative Cloud Sync
Lightroom’s power comes from cloud integration:
- Edits sync across all devices
- Full-resolution backups
- Shared albums for collaboration
This reinforces universal accessibility.
6.2 Camera and Device Compatibility
Lightroom App Latest Version Apk Lightroom supports virtually all major camera brands and RAW formats, from DSLRs to mirrorless systems and even drones.
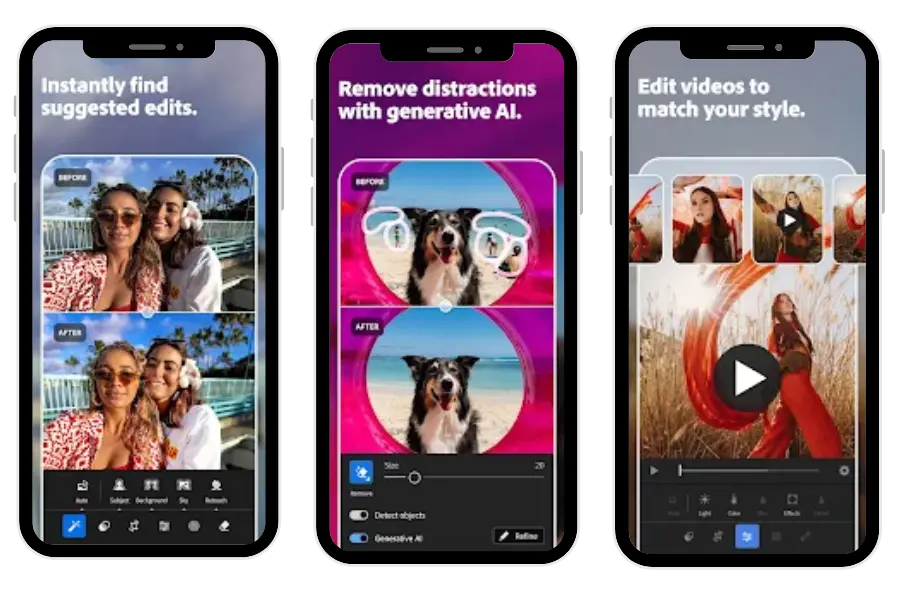
6.3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Recent AI features include:
- Auto subject selection
- AI sky replacement masking
- Object masking
- Adaptive presets
These drastically reduce manual editing time.
Chapter 7: Cultural and Industry Impact
7.1 Influence on Social Media Aesthetics
Lightroom presets have shaped the visual identities of millions of social media users. Entire brands have been built around specific Lightroom looks.
7.2 Educational Impact
Lightroom has become a cornerstone of online photography education. Platforms like YouTube, Skillshare, and TikTok host thousands of tutorials, and the Discover tab in Lightroom lets users learn by examining others’ edits.
7.3 Contribution to Creative Entrepreneurship
Through selling presets, offering editing services, and teaching workflows, Lightroom has become part of a new creative economy.
Conclusion
Lightroom App Latest Version Apk Adobe Lightroom has evolved from a desktop cataloging tool into a global creative platform that empowers photographers across every skill level. Its combination of non-destructive editing, intuitive user experience, mobile accessibility, and advanced tools makes it essential for both professionals and hobbyists.
Link Here
Lightroom not only enables technical precision but fosters creativity, storytelling, and personal expression. Whether used for professional events, commercial shoots, travel photography, or casual mobile edits, Lightroom remains one of the most influential tools in the world of digital imagery.